5 Ways Augmented Reality is Changing Engineering
Read a summary using the INOMICS AI tool
Photo Credit: Rahedesign, Wikimedia Commons
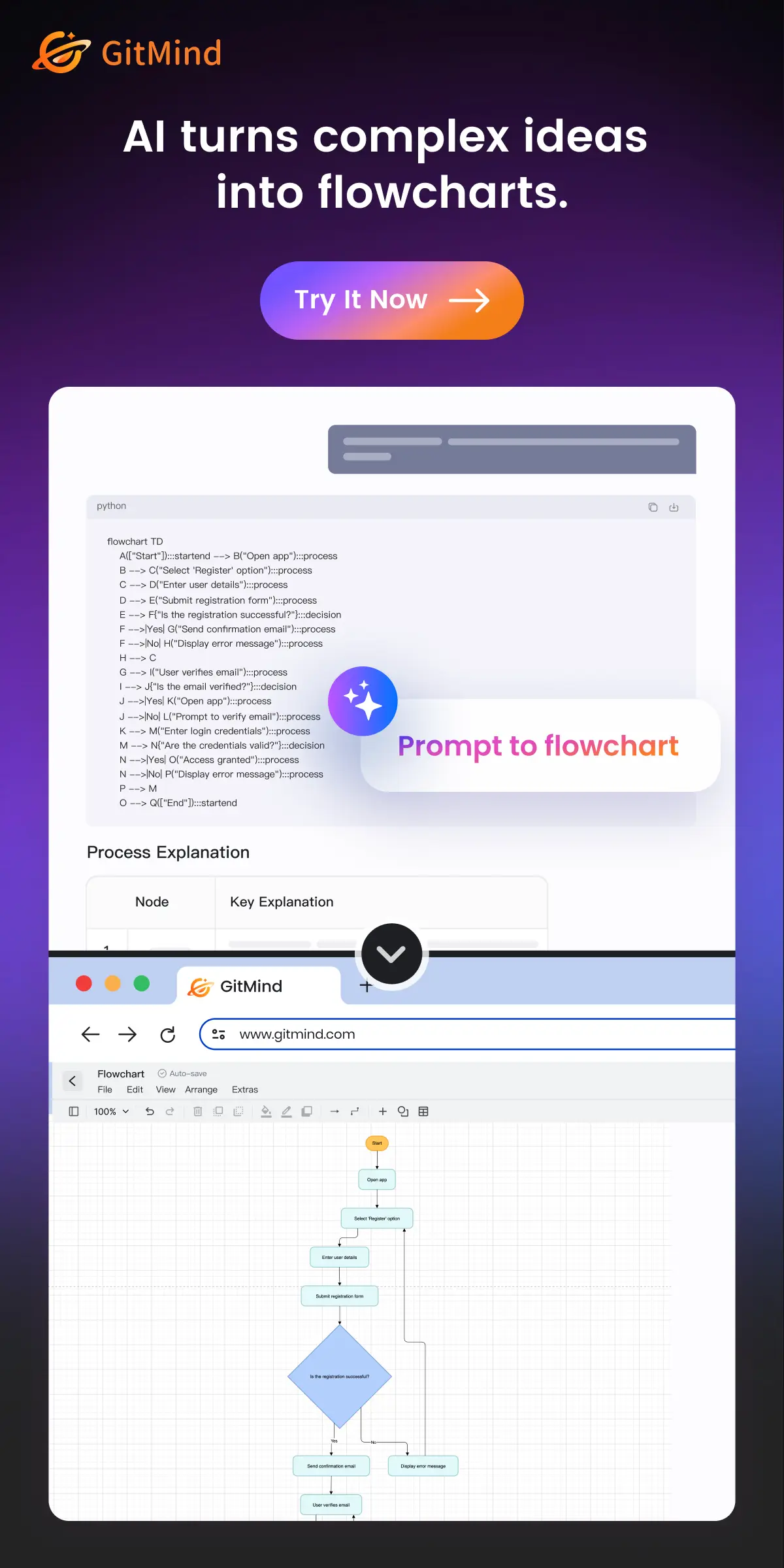
As technology advances at a phenomenal rate throughout the last decade, we have seen an increase in the use of augmented reality by the engineering industry. Augmented reality, or AR, is a direct or indirect real-time view of a physical, real-world environment whose elements are supplemented by computer-generated sensory input such as video, images, graphics, sound, or GPS data. And it certainly changes the way engineers go about their daily responsibilities. Here are 5 ways augmented reality is changing engineering. For more helpful engineering advice, news and career opportunities, make sure you subscribe to NewEngineer.com.
Increasing the ease of conceptualization
Much of the engineering and manufacturing industry is founded on the need for conceptualization. CAD software and showroom or in-home tours are used to present new concepts or remodeling options. AR significantly increases the ease of conceptualization thanks to the visual power and lifelike realities presented by VR headsets.
Streamline Production Downtime
Driving operational efficiency results in reduced production downtime, quickly identifying problems, and keeping processes moving. With augmented reality technology, engineering and manufacturing operations can be synched and streamlined to update engineers and maintenance teams in real time. This allows them to analyze and resolve the issue without disrupting production.
Decrease complexities of learning new skills
Using AR to train engineers for certain applications is becoming an important part of certain disciplines, especially in the field of biology and chemistry. The technology allows engineers to work in an almost-realistic situation and gain real-life experience with complex machines, bio-organisms, and chemicals without exposing themselves or others to any type of threat. In the field of biological engineering – AR makes virtual deconstruction possible to allow us to see just how all the parts come together and their varying significances.
Enhance remote-control capabilities for any application
The remote-control-application possibilities with AR are nearly limitless. This is great for applications that might be dangerous, such as dealing with radioactive materials, inspecting explosive devices and experimenting with different chemicals. The VR headset provides a far more lucid experience that transcends the simple applications of using a video feed and remote controller. That experience allows engineers to behave and respond to stimuli occurring in the environment as if they were present, without actually having to put themselves directly in the situation or in harm's way.
Replicate and map foreign environments
Another way that AR is changing engineering is through the replication and mapping of foreign environments. As urban areas increase in size and capacity, civil engineers feel the need to quickly and effectively design and construct new buildings all over the world. Sometimes, the logistics of actually visiting the place of development are more complicated than construction itself. This is where AR comes in, allowing engineers to virtually walk the streets of any city with not a soul in sight, or explore the area of development from every possible perspective. The presentation of foreign and new environments will allow engineers to spend less time mapping them out and more time brainstorming how to improve space through creative, cost-efficient and reliable structural developments.
Augmented reality technology certainly is the next frontier in the field – one that aids industrial manufacturing and engineering to speed up production, enhance communication and collaboration, and provide accurate data and reports across sectors.
Recommended articles
The 5 Biggest Engineering Mistakes of the 20th Century
The 10 Best Engineering Blogs You Must Read
Top 10 Postgraduate Engineering Summer Schools 2017
-
- Mid-Level Industry Job
- Posted 2 months ago
Configuration Manager - Accelerators and FCC Study (EN-ACE-CL-2025-207-LD)
At CERN in Genève, Svizzera -
- Programma di Master
- Posted 6 months ago
Master in Statistics, Data Intelligence, and the Foundations of the Sciences
Starts 15 Sep at Università Politecnica delle Marche in Ancona, Italia -
- Practitioner / Consultant Job
- Posted 1 week ago
GRADUATE STRUCTURAL ENGINEER
At Conrad Consulting in Coventry, Regno Unito